Ministry of Health Malaysia 10131924. 400 300 200 100 0 Tuberculosis TB not only had the third highest incidence rate 808 per 100 000 population of all communicable diseases in 2017 but also accounted for the highest mortality rate 65 per 100 000.
This entry lists major infectious diseases likely to be encountered in countries where the risk of such diseases is assessed to be very high as compared to the United States.
. Malaysia - Health Indicators. In 1999 the Nipah virus outbreak killed 105 Malaysians while the SARS outbreak of 2003 claimed only 2 lives. This survey was carried out by Institute for Public Health IKU to determine the prevalence of non-communicable diseases risk factors for non-communicable diseases healthcare demand as well as the health literacy in Malaysia.
Use the links below to access all documents pertaining to surveys implemented by the country. Ministry of Health Malaysia. This was then followed by the National Strategic Plan for Non-Communicable Diseases NSP-NCD 2016-2025 published in 8.
Obesity increasingly and disproportionately. The prevalence of non-communicable diseases NCDs and NCD risk factors in Malaysia have risen substantially in the last two decades. The estimated costs are those incurred as a result of NCDs in the 2017 Malaysian population.
This paper outlines the primary health. Mortality and global health estimates Sustainable development goals Millennium Development Goals MDGs Health systems Malaria Tuberculosis Child health Infectious diseases Neglected Tropical Diseases World Health. Centre for Nutrition Epidemology Research.
Coronavirus disease COVID-19 Ebola virus disease. The survey series is commissioned by the Ministry of Health to provide reliable information on the health and factors related to health of people living in Malaysia. Noncommunicable diseases NCDs such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease pose a threat to well-being and economic development worldwide.
Communicable Diseases in Malaysia Table 1 shows the current trends and status of our communicable diseases during the period 1983 to 1989568 It can be observed from Table 1 that there has been an increase in food and water borne diseases like cholera food poisoning viral hepatitis and typhoid during the period 1983 to 1987. This family contains over 70 related but distinct viruses of which most are insect. Centre for Burden of Disease Research.
Monday 09 May 2022. To strengthen Malaysias response to the increasing burden of NCDs the National Strategic Plan for Non-Communicable Diseases NSP-NCD 2010-2014 was first published in. Bacterial diarrhea vectorborne diseases.
The Malaysian Ministry of Health responded by implementing The National Strategic Plan for Non-Communicable Diseases NSP-NCD 2010-2014 and the NCD Prevention 1Malaysia NCDP-1M programme. The Malaysian Ministry of Health responded by implementing The National Strategic Plan for Non-Communicable Diseases NSP-NCD 2010-2014 and the NCD Prevention 1Malaysia NCDP-1M programme. Top 10 causes of death.
Communicable diseases NCD and healthcare demand HCD with the other years focusing on other priority areas as determined by the Ministry of Health Malaysia. Contains data from World Health Organizations data portal covering the following categories. COVID-19 pandemic is the greatest communicable disease outbreak to have hit Malaysia since the 1918 Spanish Flu which killed 34644 people or 1 of the population of the then British Malaya.
Dengue fever water contact diseases. KUCHING June 14 Non-communicable diseases NCD led by cardiovascular issues cancer and diabetes are the main causes of deaths in the country including Sarawak said Deputy Premier Datuk Seri Dr Sim Kui Hian. This revised and updated third edition of the Case Definitions for Infectious Diseases in Malaysia is timely and will serve as an invaluable guide to assist all medical professionals to notify infectious diseases in a prompt and systematic manner.
Ministry of Health Malaysia. Best viewed with Internet Explorer 10 and above Mozilla Firefox 40 above or Google Chrome 40 and above or Safari 4 and above with minimum resolution at 1024 x 768. The series aims to.
The findings of NHMS 2019 has recently been released. The prevalence of non-communicable diseases NCDs and NCD risk factors in Malaysia have risen substantially in the last two decades. Centre for Occupational Health Research.
Major infectious diseases. The three NCD categories namely cardiovascular disease. Yellow fever virus is a member of the Flaviviridae family of viruses.
Infectious Diseases under the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases Act 1988 Act 342. This report quantifies the productivity losses and burden of disease costs that stem from the three largest NCD categories in Malaysia. Like dengue it is also one of the most common infectious diseases primarily impacting those living under the strain of poverty in Malaysia.
The mosquitoes usually bite during daylight hours. Intermediate 2020 food or waterborne diseases. Communicable Disease Hand Foot Mouth Disease HFMD.
In 2012 the World Health Organization WHO set a comprehensive set of nine global voluntary targets including the landmark 25 by 25 mortality reduction target and 25 indicators. We are generating evidence that will help shape the expansion of this pilot program and eventually inform noncommunicable disease policies in Malaysia and beyond. Centre for Communicable Disease Research.
Incidence rates of communicable diseases 20092017. Yellow fever is a serious and fatal disease that is transmitted by the bite of the Aedes aegypti mosquitoes that transmit dengue in Malaysia. Burden of disease in Malaysia With regard to the burden of disease there were more reports of non-communicable diseases as health risks as opposed to the number of communicable disease cases.
Dr Sim who is Minister of Public. As we aim for the survey findings to reach out to public and. Tuberculosis TB Tuberculosis TB is an air-borne infection affecting the lungs.
Centre for Non-Communicable Disease Research. This page provides a summary of all NCD surveillance activity for Malaysia. Overcrowded and poorly ventilated residential areas facilitate TB in low-cost flats all around Malaysia.
WHO has also highlighted the importance of Non-Communicable Disease NCD surveillance as a key action by Member Sta.

Pin On Healthcare Architecture

Ijerph Free Full Text Tuberculosis And Non Communicable Disease Multimorbidity An Analysis Of The World Health Survey In 48 Low And Middle Income Countries Html

Medobal Proudly Invites Healthcare Professionals Around The World To The International Conference On Ayu Medical Tourism Traditional Medicine Medicine Journal

Germs Are Not For Sharing Hygieneslogans Hygiene Sayings Healthslogans Cleaness Washing Hygiene Quotes Health Slogans Cleanliness Quotes
Malaysia Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Outbreak Continues To Grow In 2022 Nearly 32k Cases Reported To Date Outbreak News Today
Ivermectin Does Not Reduce Risk Of Severe Illness From Covid 19 Malaysia Study Outbreak News Today

How The World Got Hooked On Palm Oil Palm Oil Food Industry Oils

Certified Environmental Hygienists Phillip Fry And Hank Taylor Have Discovered Extensive Toxic Mold Growth In The Majority Workplace Mold Inspection Hygienist
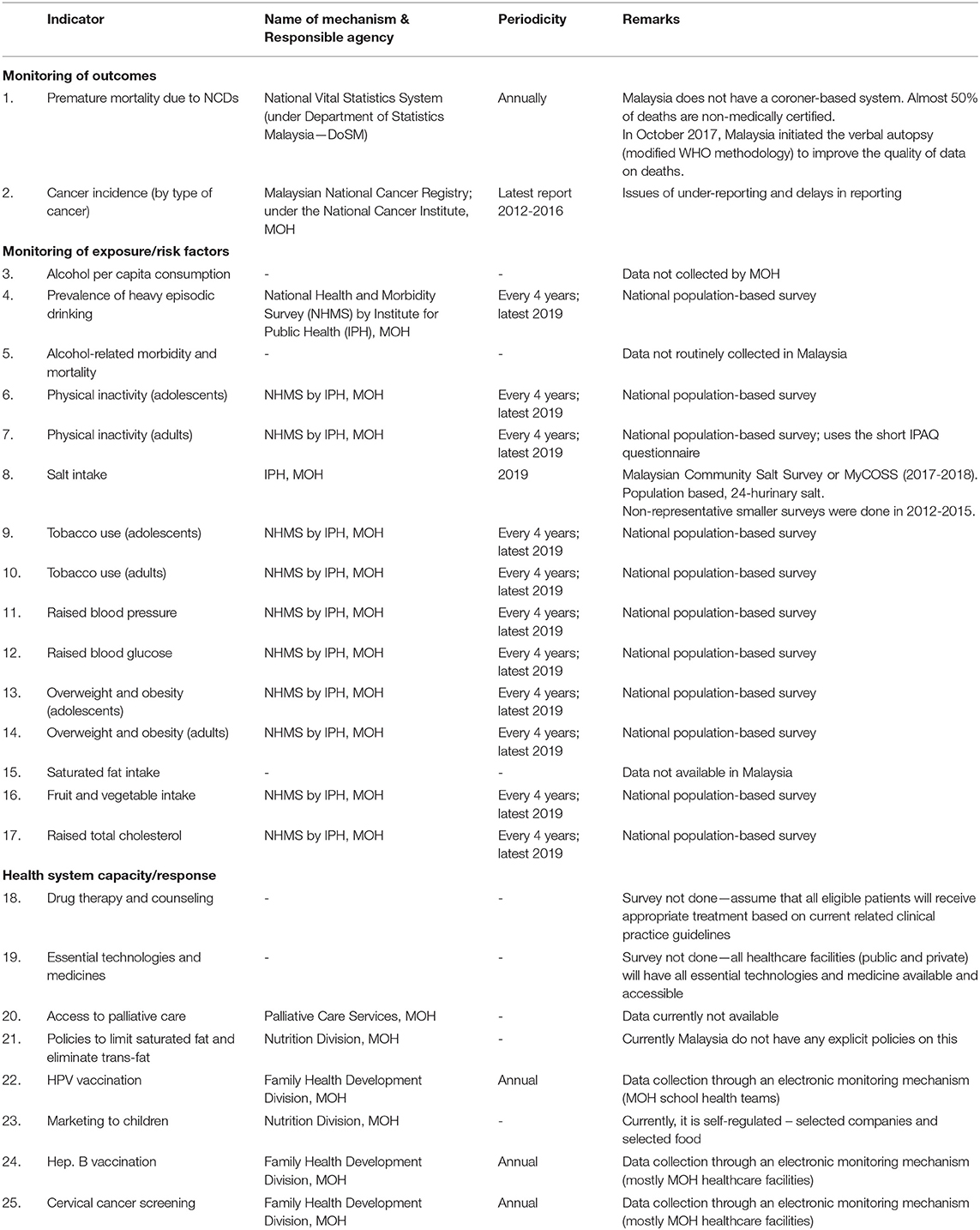
Frontiers Non Communicable Disease Surveillance In Malaysia An Overview Of Existing Systems And Priorities Going Forward Public Health

List Of Communicable Disease With Its Infectious Agent Download Scientific Diagram

Iecbbb 2020 Education Domain Biotechnology Challenges And Opportunities

The Global Infectious Disease Threat And Its Implications For The United States
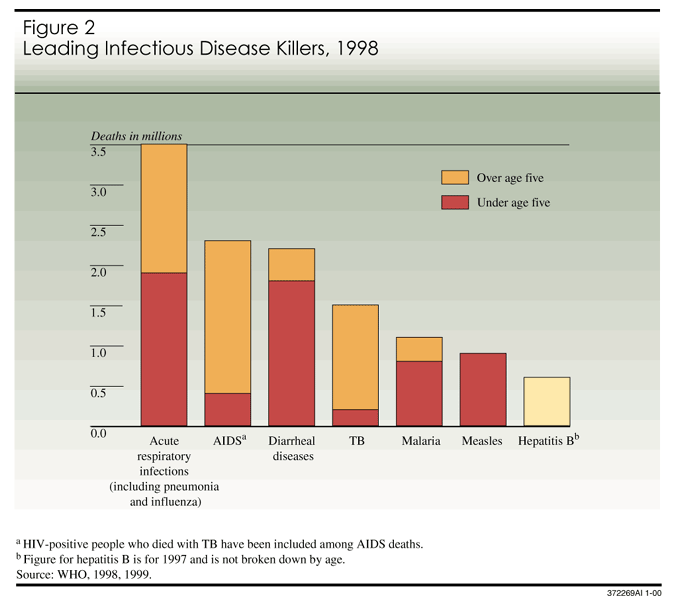
The Global Infectious Disease Threat And Its Implications For The United States





